- Recommended name
- Pinnatoxin E
- Synonyms
- Pinnatoxin-E
- Recommended acronym
- PnTX-E
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Vulcanodinium rugosum
- Note
- Initially isolated from oysters (Magallana gigas, formerly Crassostrea gigas) and razor fish (Pinna bicolor) by Selwood et al., 2010 in New Zealand and Australia, the toxins were also rapidly identified in sediment-derived strains of dinoflagellates (Rhodes et al., 2010), later identified as Vulcanodinium rugosum (Nézan and Chomérat, 2011 & Rhodes et al., 2011)
Vector Species
- Name
- Magallana gigas
- Note
- Initially isolated from oysters (Magallana gigas, formerly Crassostrea gigas) and razor fish (Pinna bicolor) by Selwood et al., 2010 in New Zealand and Australia, the toxins were also rapidly identified in sediment-derived strains of dinoflagellates (Rhodes et al., 2010), later identified as Vulcanodinium rugosum (Nézan and Chomérat, 2011 & Rhodes et al., 2011)
- Name
- Pinna bicolor
- Note
- Initially isolated from oysters (Magallana gigas, formerly Crassostrea gigas) and razor fish (Pinna bicolor) by Selwood et al., 2010 in New Zealand and Australia, the toxins were also rapidly identified in sediment-derived strains of dinoflagellates (Rhodes et al., 2010), later identified as Vulcanodinium rugosum (Nézan and Chomérat, 2011 & Rhodes et al., 2011)
References
- Selwood et al.,, 2010
- Selwood, A.I., Miles, C.O., Wilkins, A.L., van Ginkel, R., Munday, R., Rise, F., McNabb, P., 2010. Isolation, Structural Determination and Acute Toxicity of Pinnatoxins E, F and G. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(10), 6532-6542.
- Rhodes et al.,, 2010
- Rhodes, L., Smith, K., Selwood, A.I., McNabb, P., van Ginkel, R., Holland, P.T., Munday, R., 2010. Production of pinnatoxins by a peridinoid dinoflagellate isolated from Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 9(4), 384-389.
- Nézan & Chomérat,, 2011
- Nézan, E., Chomérat, N., 2011. Vulcanodinium rugosum gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), un nouveau dinoflagellé marin de la côte méditerraneenne française. Cryptogamie, Algologie 32(1), 3-18.
- Rhodes et al.,, 2011
- Rhodes, L., Smith, K., Selwood, A., McNabb, P., Munday, R., Suda, S., Molenaar, S., Hallegraeff, G., 2011. Dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum identified as the causative organism of pinnatoxins in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Phycologia 50(6), 624-628.
- Structure
-
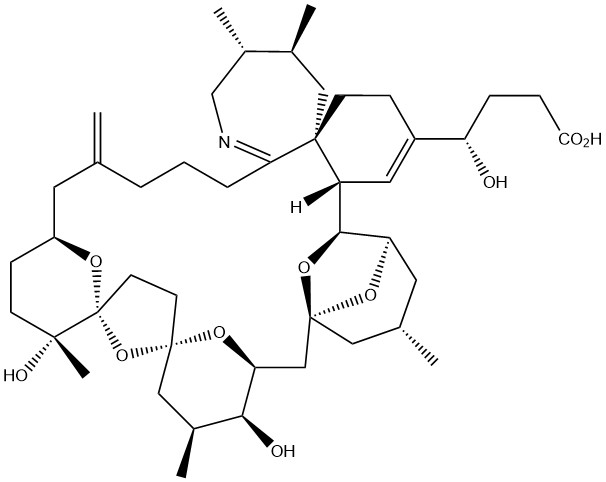
- Formula
- C45H69NO10
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 783.49215
- Molfile
- see chemfiles
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- C[C@@H](CN=C1CCCC(C[C@@H]2CC[C@](O)(C)[C@](O2)(O3)CC[C@@]3(O4)C[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H]4C5)=C)[C@@H](C)C[C@@]61[C@]([C@@H]7O[C@]85C[C@@H](C)C[C@H]7O8)([H])C=C([C@@H](O)CCC(O)=O)CC6
- Alternative SMILES
- n/a
- InChi key
- UHUWABBDQXWCRL-YUHUXZIXSA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C45H69NO10/c1-26-8-7-9-37-42(22-28(3)30(5)25-46-37)15-12-31(34(47)10-11-38(48)49)20-33(42)40-35-19-27(2)21-44(53-35,55-40)24-36-39(50)29(4)23-43(54-36)16-17-45(56-43)41(6,51)14-13-32(18-26)52-45/h20,27-30,32-36,39-40,47,50-51H,1,7-19,21-25H2,2-6H3,(H,48,49)/t27-,28-,29-,30-,32-,33+,34-,35+,36-,39-,40-,41+,42+,43-,44-,45+/m0/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- Unknown
- Chem files
- chemfiles/PnTX-E.cdxml chemfiles/PnTX-E.mol
- Certified
- True
- Certified links
-
- Merck
Trace Cert - certification
- Merck
- Non certified reference material
- True
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- n/a
- Risk assessment
- Unknown
- Molecular targets known
- True
- Molecular targets
- Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- Unknown
- TEF available
- False
- Notes
- Isopinnatoxins have been described for PnTX-E, -F, -D and -H. These isoforms are formed through acid-catalyzed ring-opening of the D-ring and transformation of the 6-membered D-ring into a five-membered D-ring thanks to an OH-group at C22. (Selwood et al., 2025)
References
- Selwood et al.,, 2025
- Selwood, A.I., Miles, C.O., Wilkins, A.L., Rise, F., Finch, S.C., van Ginkel, R., 2025. Structural Characterization of Pinnatoxin Isomers. Mar. Drugs 23(3), 11.
- Philipp Hess
- Contact